Georgia Sees Increase in Measles Cases in 2018
Monday, June 11

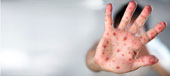
According to Paata Imnadze, the deputy director of the Center for Disease Control, the measles distribution has significantly increased in comparison with 2017, when only tens of cases were observed.
Imnadze believes that the media has to remind the society more frequently that the immunization is free and everyone can get vaccinated to prevent the disease from spreading.
“At least 95% of population should be vaccinated to prevent the spread of measles. Vaccination of people under 40 is free but if they are over 40 and do not know if they are vaccinated, we will serve them for free too,” Imnadze said, calling on the society to get vaccinated.
Measles is a highly contagious infection caused by the measles virus. It is an airborne disease which spreads easily via air and also through saliva or nasal secretions. Nine out of ten people who are not immune and share living space with an infected person will catch it.
Initial signs and symptoms typically include fever, often with temperature higher than 40 °C (104.0 °F), cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Two or three days after the start of symptoms, small white spots may form inside the mouth, known as Koplik's spots. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the symptoms are revealed. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Complications occur in about 30% and may include diarrhea, blindness, inflammation of the brain, and pneumonia among others.
